Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is the involuntary leakage of urine during activities such as coughing, sneezing, sudden changes in position or sports. It affects at least one third of women and can significantly impair their quality of life.
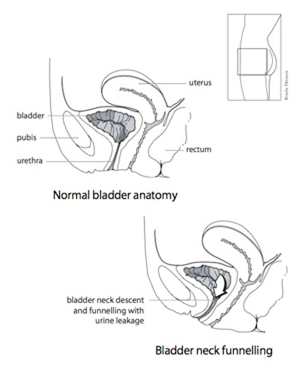
The bladder normally stores urine until emptying is desired. SUI is thought to result from the loss of support of the urethra (urinary passage) allowing it to funnel open or descend or both during straining. This results in urine leakage.
Stress incontinence differs from other forms of urinary incontinence (“leakage”) including:
Some women may have a mixture of several kinds of urinary incontinence.
A physician can clarify incontinence problems by asking questions and performing some investigations. Different forms of urinary incontinence require quite different treatments.

Several factors increase the chances of developing SUI, including:
The investigation of SUI begins with a thorough questioning regarding normal voiding patterns and problems of urinary leakage. The timing and frequency of accidents and the need to wear protection should be clarified.
A examination with full bladder during coughing and straining can demonstrate the incontinence. Measurements can be taken of bladder capacity, urine flow, and how well the bladder can empty.
A urine sample may be obtained to exclude bladder infection and other urinary problems. Other more sophisticated tests may be required in some cases and will be explained by a doctor. This may include a visual examination of the bladder (cystoscopy). Urodynamic assessment, where pressures in the bladder and its outlet are measured during filling, emptying and straining, may be recommended.
Non-surgical measures such as pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises), biofeedback and weight loss may be helpful in mild cases.
Medications may be useful to control some of the problems that accompany SUI. Estrogen (female hormone) replacement in postmenopausal women may restore the quality of the tissues around the urethra. Bladder overactivity with abnormal frequency and urgency of urination may improve with medication.
Some women benefit from wearing a vaginal ring or pessary, much like a contraceptive diaphragm, to support the bladder outlet.
Injection of material (eg. collagen) around the urethra may be helpful in some patients. Repeat injections may be required.
Surgery may be appropriate for those women in whom persistent SUI is very bothersome. Several surgical techniques are available to correct SUI. Bladder outlet supporting sutures are placed through a lower abdominal incision in the Burch or Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz procedures. The problem may also be corrected with a “sling” procedure, in which a supporting strip of tissue or synthetic material is placed, often through a small vaginal incision. Your surgeon will recommend the procedure most appropriate for your condition and review the specifics of any surgery planned.
Stress urinary incontinence is a common problem in women having a definite negative impact on their quality of life. Fortunately, it can often be helped with lifestyle changes, exercises and, sometimes, surgery.