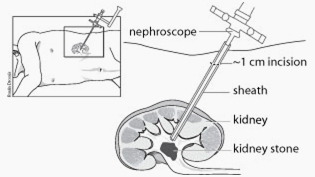
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a surgical procedure in which kidney stones are removed using a scope passed through a small skin incision made in the flank or the back into the kidney containing the stone(s).

The risk of bleeding is increased in patients taking blood thinners, aspirin, some arthritis medications, or many herbal supplements. These drugs must be stopped prior to surgery. Please discuss this with your doctor. Pre-operative antibiotics may be recommended. We may require special X-rays prior to the procedure to help with planning how to reach and remove all of your stones.
PCNL first requires developing an access or channel through the skin to the kidney allowing the introduction of surgical instruments. There are different methods of establishing this access into the kidney. In some cases, this part of the procedure is performed under local anaesthetic (“freezing”) by a specialist in the xray department prior to the stone removal procedure. Otherwise, this part of the procedure can be performed at the same time as the stone removal procedure, usually under general anethesia (you are “put to sleep”). This access is often obtained by first passing a thin needle into the kidney. Once this access is performed a wire or tube will be left until the second part of the surgery takes place. Some surgeons prefer to gain this access from inside-out by passing a thin needle under x-ray control through the bladder up to the kidney and out through the skin. In some cases, more than one access tract is required to reach all of the stones.
In the operating room, the access tract is stretched to allow the introduction of surgical instruments. Once the tract is dilated up to about one centimetre(less than half an inch) a plastic tube is then placed into the kidney. An operating scope (nephroscope) is then passed through the tube into the kidney on to the stone(s). Small stones can be removed with a grasper. Larger stones need to be broken up before they can be removed. An attempt is made to remove all of the stones. In some patients this may not be possible and may require additional treatment.
Once stone removal is complete, a small tube may be left in the kidney, through the access tract to allow urine to drain. This tube usually can be removed in a few days. In some, temporary kidney drainage is obtained with an internal drainage tube. Aureteric stent is an internal drain running from the kidney to the bladder. A bladder drainage catheter may be left for a few days.
The procedure is usually recommended for patients with kidney stones which are too large or numerous for shock wave lithotripsy, in which stones are broken-up non-surgically. The procedure involves two major steps. The first is establishing a tract or access path into the kidney containing the stones, and the second is stone removal using special operating instruments.
A hospital stay of one to three nights is usually all that is required. In some patients a longer hospital stay is necessary.
Recovery from percutaneous stone removal is usually rapid. Patients may return to normal but not excessively strenuous activity as soon as they leave hospital. Return to work is usually possible within a week after discharge from hospital.
Major complications from PCNL are uncommon, but, potentially, these can be serious. Possible complications are:
You may be asked to take antibiotics after percutaneous stone removal. Usually antibiotics are only taken for a week or less, but in some patients a prolonged course of antibiotics may be recommended. A follow up visit with us will be recommended. At that time you will have x-rays to determine if there are any residual stones.
PCNL is a surgical procedure to safely and successfully remove large stones from the kidney through a small skin incision allowing rapid recovery.