Renal colic is the name given for the pain caused by passing a kidney stone. A kidney is found in each flank under the ribs in the lower back. The kidneys play an important role in eliminating waste products from the body. These waste products normally remain dissolved in the urine as it passes from the kidney through its drainage system (calyces, renal pelvis and ureter) into the bladder.
Kidney stones are crystalline particles that form in the urine, often producing pain when they obstruct urine drainage from a kidney. About one in ten Canadians will develop a kidney stone, and of these, half will form more than one over their lifetime. This problem is more common in men than in women, and, it occurs rarely in children.
A kidney stone may remain silently in the kidney for many months or years before being discovered incidentally on imaging studies performed for various reasons. In other cases, a stone may obstruct drainage of urine from a kidney causing pain. This pain can range from a mild and barely noticeable discomfort, to severe cramping or stabbing pain that requires hospitalization for control. Renal colic may wax and wane in severity, coming and going with episodes of pain lasting 20 to 60 minutes. Patients frequently feel the need to move around in order to find a more comfortable position.
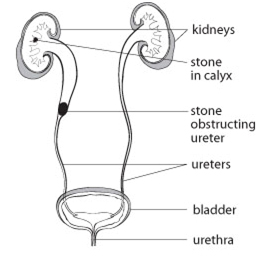
The pain occurs on the side of the stone but its precise location depends upon where the stone becomes lodged in the kidney or ureter. The nature and location of the pain may change as the stone migrates down the ureter toward the bladder. Renal colic will often start in the flank (between the ribs and hip) or lower back but it can also be felt in the lower abdomen, groin, genitals or inner thigh. The pain of renal colic may be associated with nausea, vomiting, and frequent or urgent urges to urinate, which may be painful. Blood in the urine (hematuria) occurs frequently with kidney stones. This blood may be visible or microscopic.
The diagnosis of renal colic may be suspected by the description of pain experienced supported by simple blood and urine tests. Some type of medical imaging is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the size and location of the kidney stone. A CT scan is the most commonly used imaging test to diagnose a kidney stone and determine its size and location. Other tests may include ultrasound imaging or IVP (intravenous pyelography), which involves an intravenous injection of “dye” that is excreted into the urine from the kidneys demonstrating their appearance, function and drainage. Many kidney stones can be seen on a simple x-ray of the kidneys, ureter and bladder (KUB). This can be very useful in following the progress of a stone as it passes through the ureter.

The severity of the pain associated with a kidney stone often prompts one to seek care at a hospital emergency room or urgent care clinic. Once the diagnosis of renal colic is confirmed, efforts are made to control pain. This may be achieved with oral painkillers (e.g. acetaminophen with codeine) or intravenous medications such as morphine. Anti-inflammatory medications (e.g. indomethacin or diclofenac) in tablet or suppository form may also be useful.
Many kidney stones are small enough to pass out with the urine in a few days. Others may take several weeks to pass. A physician can often predict how likely the stone will pass on its own based on its size and location. Once the stone drops into the bladder, the pain will quickly resolve. Drinking plenty of water (2 to 3 liters per day) will encourage urine flow and may assist stone passage. A physician may recommend a daily oral medication called an alpha-blocker (e.g. tamsolusin or Flomax™) to help the muscle of the ureter relax and facilitate stone passage.
The majority of kidney stones cannot be dissolved. However, one form (uric acid stone) may occasionally disintegrate when the urine is made less acid with medication (alkalinization). It is important to try to collect any stone passed so that it can be analyzed to determine its chemical make-up. This will allow a physician to advise measures to reduce the risk of further stone formation.
When pain is difficult to control or the stone becomes lodged and fails to pass, a physician will recommend additional treatment. A fever (greater than 38.5oC) or chills suggests the possibility of infection and indicates the need for more urgent treatment. There are a number of ways to treat a stone causing renal colic. The type of treatment recommended will depend on a number of factors, including your general health, as well as the type, size and location of your stone.
Shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) (“stone crushing”) is a non-surgical treatment in which high energy shock waves are used to pulverize a stone into smaller fragments which may pass more easily and with less pain. A special machine (which may not be available at your local hospital) is used to generate shock waves. X-rays or ultrasound are used to focus the shock waves precisely on the stone. The shock waves pass harmlessly through body tissues until they hit the hard stone causing it to break up. The fragments can then flush out more easily in the urine. SWL may not be appropriate for larger stones or for those that are difficult to locate on X-ray.
Ureteroscopy is a procedure in which a narrow telescope is passed through the urethra (urinary tube) and bladder, into the ureter up to the stone.
This surgical procedure requires some form of anaesthesia. Most cases will require a general anaesthetic (you are “put to sleep”) or spinal anaesthetic (a needle in the back “freezes” the patient below the waist and remains conscious). Some cases can be performed comfortably with sedation alone. Once visualized through the scope, the stone can then be removed by trapping it in a wire “basket” and carefully pulling it out. Various instruments including lasers are available to fragment larger stones and allow their passage or removal. Upon completion of the procedure, a thin plastic tube (ureteric stent) may be placed temporarily in the ureter to prevent blockage while any swelling resolves. Overnight hospitalization may be recommended.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a surgical procedure in which kidney stones are removed using a scope passed through a small skin incision made in the flank or the back into the kidney containing the stone(s). The procedure is usually recommended for patients with kidney stones which are too large or numerous for shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopy. This procedure is carried out in a hospital or surgical centre with appropriate anaesthetic and hospital admission for a few days.